
The foundations of buildings bear on and transmit loads to the ground. The foundation is that part of walls, piers and columns which is in direct contact with and transmit loads to the ground.
The foundations of varying types depending upon load requirement, ground conditions and prevailing practices in the region. A strip foundation is a continuous strip of concrete under walls, an isolated footing is a concrete isolated base under piers and columns, a raft foundation is a continuous base under the whole of the building and a pile is a concrete column or pillar cast in or driven into the ground to support a concrete base or ground beam.
Stone wall footing Reinforced Concrete Footing
The Functional Requirements of foundation in general :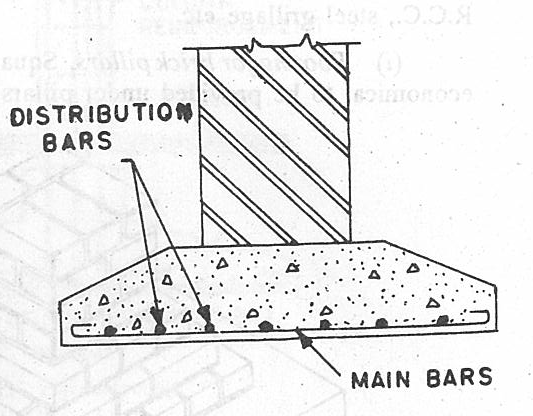
• Strength and stability
• Resistance to ground moisture
• Resistance to the passage of heat
Foundation Types
Strip foundation 
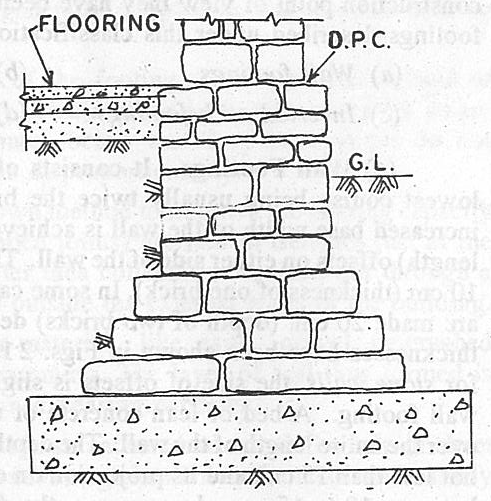
Strip Foundations consist of a continuous strip, mad e up of brick masonry/stone masonry/concrete formed centrally under load bearing walls. The continuous strip serves as a level base on which the wall is built and is of such a width as is necessary to spread the load on the foundations to an area of subsoil capable of supporting the load without undue compaction.
Isolated foundation 
It is sometimes economical to construct a foundation of isolate d piers or columns of brick or concrete supporting reinforced concrete ground beams in turn supporting walls, rather than excavating deep trenches and raising walls off strip foundations, some depth below ground. The isolated foundations are typical rectangular or trapezoidal block made up of reinforced concrete. In some places where burnt clay brick quality is good, these are made with burned bricks also.
Raft foundation 
The Raft foundations consist of a raft of reinforced concrete under the whole of the building designated to transmit the load of the building to the subsoil below the raft. Raft foundations are used for buildings on compressible ground such as very soft clays, alluvial deposits and compressible fill material where strip foundations would not provide a stable foundation. A typical raft foundation comprises of beam column system along with huge slab below ground.
Pile foundation 
Where the subsoil has poor or uncertain bearing capacity or where there is likely to be appreciable ground movement as with firm, shrinka ble clay or where the foundation should be deeper than stay 2 m, it is often economical to use piles.
A pile is a column of concrete either cast in or driven into the ground to transfer loads through the poor bearing soil to a more stable stratum. The piles support reinforced concrete beams off which load bearing wall are built.
Shot-bored piles
For small buildings, for example on shrinkable clays where adjacent trees or the felling of trees makes for appreciable volume change in the subsoil for some depth, it is often wise and economical to use a system of short-bored piles for foundations. Short-bored, that is short length; piles are cast in holes augured by hand or machine.
